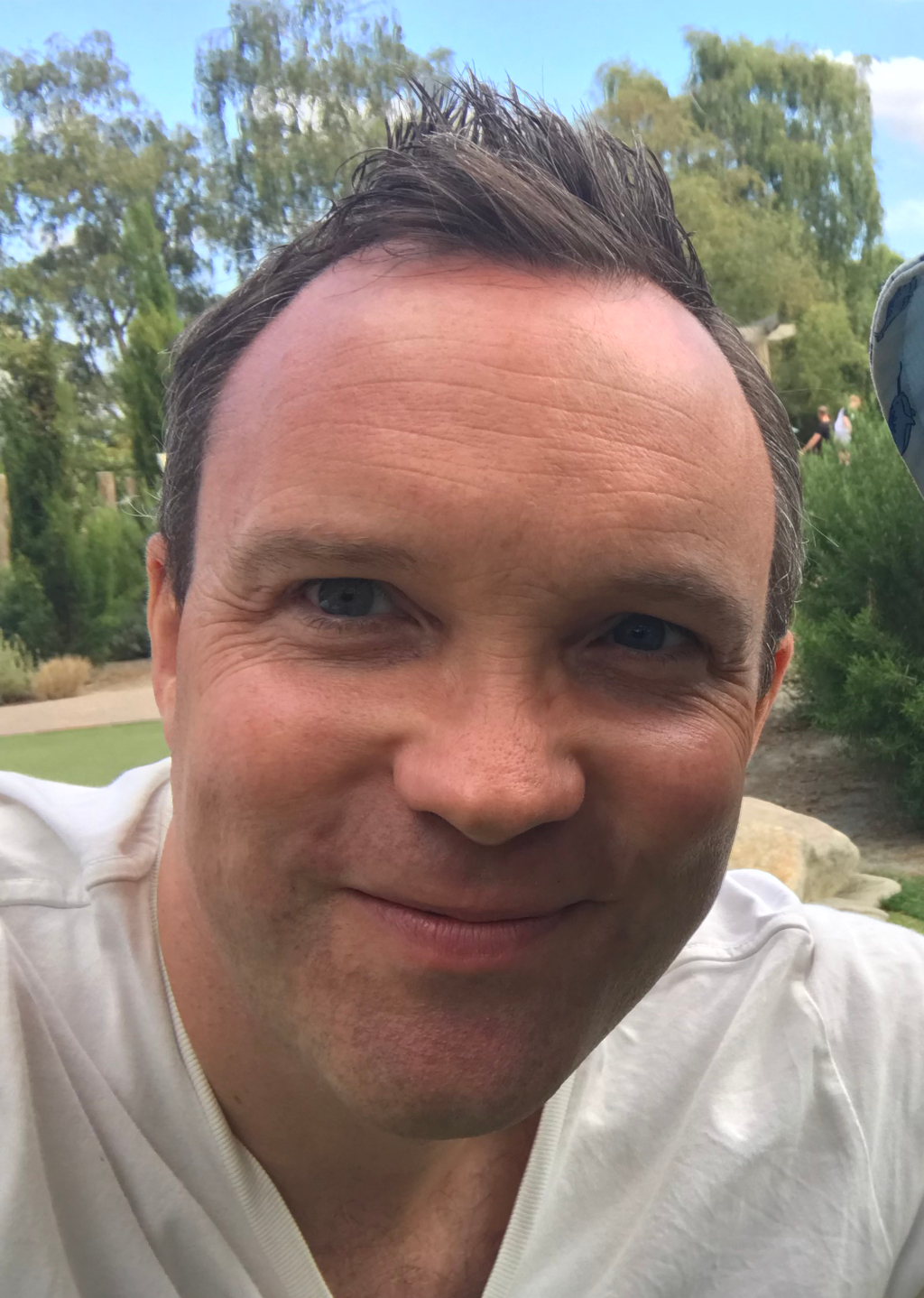
Evening shows is a painting by Paul Klee.
Paul Klee, a Swiss-born painter, engraver and designer of German nationality, was initially associated with the German expressionist group Der Blaue Reiter, and then taught at the Bauhaus, the German art school of great influence between the two wars.
Klee's heterogeneous work body can not, however, be classified according to any single artistic movement or "school". His paintings, sometimes fantastic, kids or ingenious, served as inspiration for the New York School and many other artists of the twentieth century.
Paul Klee was born by a German father who taught music to Berna-Hofwil's teachers and a Swiss mother formed as a professional singer. Encouraged by her parents, she has taken the violin at the age of seven.
His other hobbies, drawing and writing poems, were not promoted in the same way. Despite the desire of parents to pursue a musical career, Klee decided he would be more successful in visual arts, a field where he could create something that was enough to run.
Klee was essentially a spiritualist who believed that the material world was just one of the many open to human consciousness realities. Use drawing, model, color and miniature systems, all speak of their efforts to use art as a window that philosophical principle sign.
Klee admired the art of children, who seemed to create free patterns or examples above. In his work, he has often struggled to get a similar simplicity, often using bright colors inspired by an early trip to North Africa, and drawing the line to just as little studied a daily craftsman.
Klee constantly experimented with artistic techniques and expressive force of color, in the process often breaking the traditional or "academic" rules of oil painting on canvas. Klee also applied unusual paint, such as spraying and molding during his years at the Bauhaus modes. Keeping his work in the field of "ordinary" Klee also painted on a variety of daily-use materials such as canvas, cardboard and muslin.