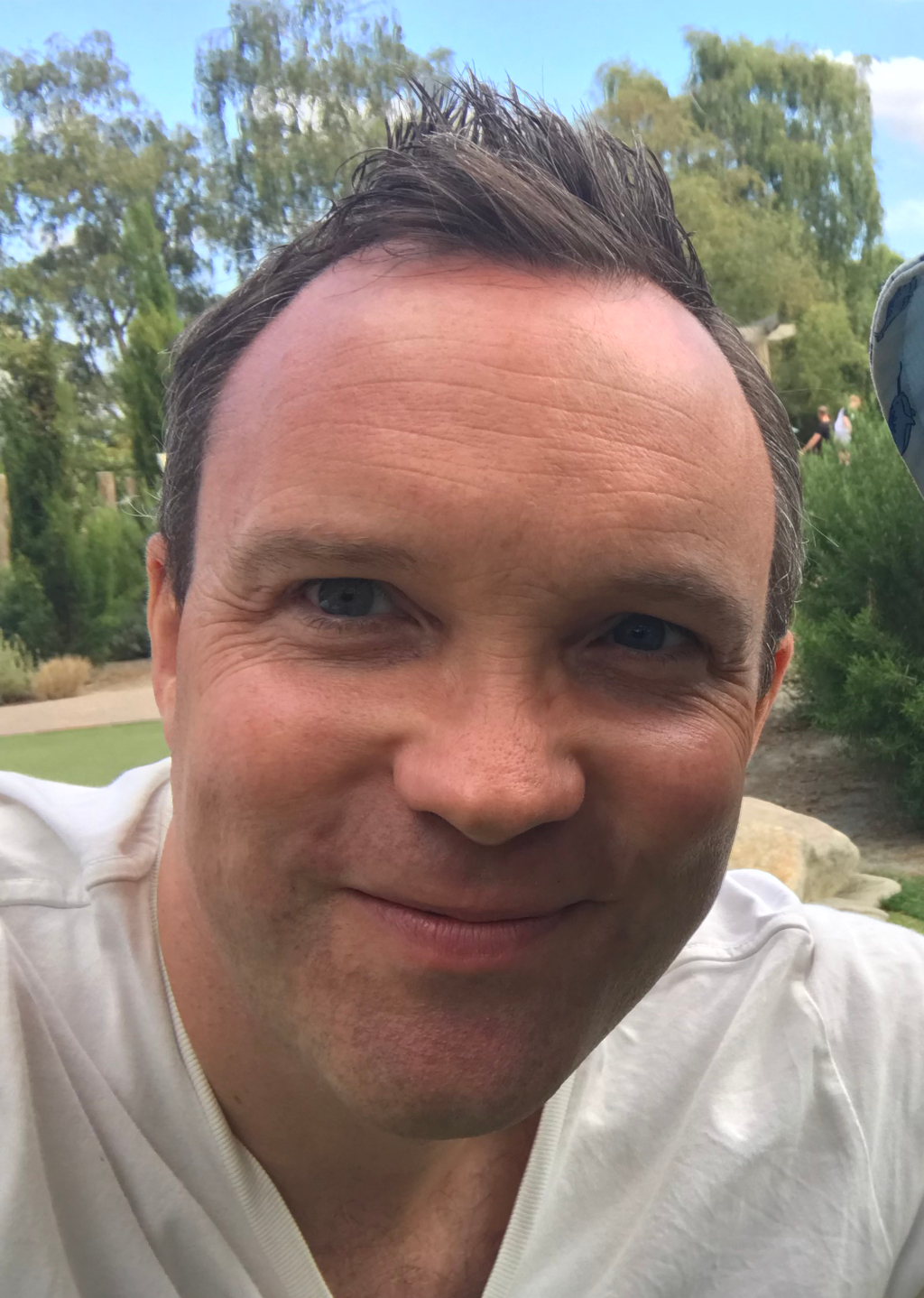
Primula by Albrecht Durer was painted in 1526. The painting is created in the artist's typical Northern Renaissance style, which he was famous for. The painting is also known as Tuft of Cowslips. Durer's used the techniques he learnt in this kind of artwork to develop his art and hone his skills.
Durer uses the gouache technique to produce the Primula. This painting mode is where the artist uses thick water-soluble paints on materials such as thick silk cardboard or plywood. The outcome is a smooth, texture-rich surface. The advantage of using this method is that it allows the artist to make corrections by diluting the dried paint then adding a new layer of pigment to alter the errors. Primula is a flower painting of the cowslip grass plant. The artwork uses a green hue predominantly. The leaves in the picture are on the ground, with the bottom sitting on a dark mound of soil. Above them are blooming bells of light green flowers, compared to the darker green of the leaves. The tips of the flowers are golden yellow with a few flower bells nestled among the leaves. The plant seems to be in the early process of wilting, with some leaves beginning to turn brown.
The pigments in the painting are rich but not vibrant as they are muted. The darker foreground and much lighter foreground bring attention to the plant as it is the main focus of the painting. The detail in the artwork is reminiscent of Durer's detail-rich paintings. The lines on the leaves make the image come alive and enhances its three-dimensional quality. The use of gouache gives a realistic representation in the picture. Durer's painting represents the plants as they appeared, which was a distinct approach during that period. This method of painting plants and nature had a significant influence on rendering flowers in art up to the 17th century.
Durer developed various techniques in his artwork. The countries he visited influenced the development of his skills. His interest in gouache was from his trips to Italy, where he was exposed to great artists such as Antonio Pollaiuolo, Mantegna, and Lorenzo di Credi. In Italy, he began to use watercolours for his paintings and produced his nature artworks depicting landscapes and animals. Primula is housed in the National Gallery of Art in Washington, D. C. and is displayed under the tag flowers. It was in the private collection of Hal O'Nians Gallery in London, England, and then gifted to Armand Hammer Collection in 1971, which then granted it to the National Gallery of Art in 1991.